🤖 AI-Powered SDLC: Building an AI Framework for Developer Experience
A practical guide to integrating AI across your Software Development Lifecycle
In large organizations, we invest a lot in engineering foundations: standards, best practices, tooling, documentation. But even when everything is in place to help teams, there’s no guarantee it will actually be followed — or maintained over time. Turnover, habits, priorities, budget constraints… the list of reasons is long.
Since the rise of AI, I’ve been genuinely excited because I see real solutions to this challenge. What excites me the most is the idea of adding a layer on top of these foundations to facilitate their adoption by teams. In the same way automated tests validate your code, I really like the idea that your specs, your documentation, and your architectural rules can validate your way of working through AI. It also helps keeping codebases aligned with the latest standards over time.
That said, there is one big pain point: AI fatigue.
Some time ago, people were talking a lot about JavaScript fatigue. Personally, I always found it exciting to discover new frameworks and architectures and try to understand what could be the next best one. AI brings a similar level of excitement — but to be honest, it is impossible to follow everything. New tools, new models, new workflows appear almost every week.
Still, we have to start somewhere.
In this article, I wanted to structure everything I’ve been learning about AI in software development — as much for myself as for you. I’ll list concrete use cases where AI can improve the Developer Experience, increase productivity, and — maybe more importantly — improve quality in a sustainable way.
🧱 Core Concepts
To understand how AI transforms the SDLC, let’s first look at the key layers that make it effective.
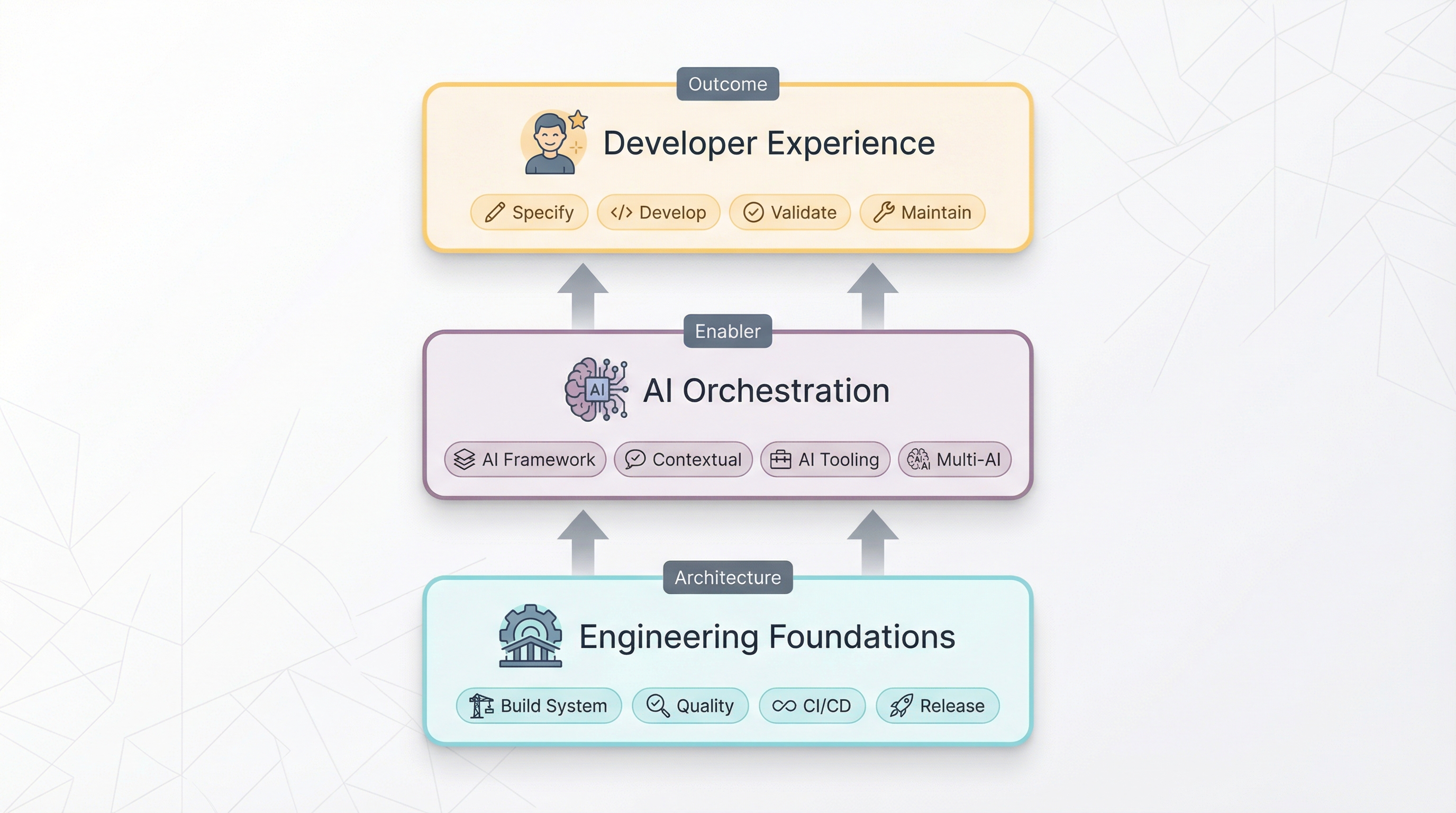
🏗️ Engineering Foundations
AI needs trusted, structured knowledge to be effective. The more organized your foundations, the more powerful AI becomes.
Key sources include:
- Codebase — Your actual code, patterns, and implementations
- Architecture — System design, boundaries, constraints, ADRs
- Design System — UI components, tokens, accessibility standards
- Dependency Graph — Project relationships and impact analysis
- CI/CD Signals — Build history, failures, flaky tests, bottlenecks
- Documentation — Conventions, onboarding guides, runbooks
- Methodologies — Agile, Scrum, SAFe, workflows, team rituals, definition of done
Organizations with clear boundaries, ownership, and conventions naturally benefit more from AI — because AI has a map, not just files.
💡 Nx as a Foundation: Nx provides structured, queryable knowledge about your workspace — project graph, generators, affected analysis — that AI tools can leverage directly via MCP.
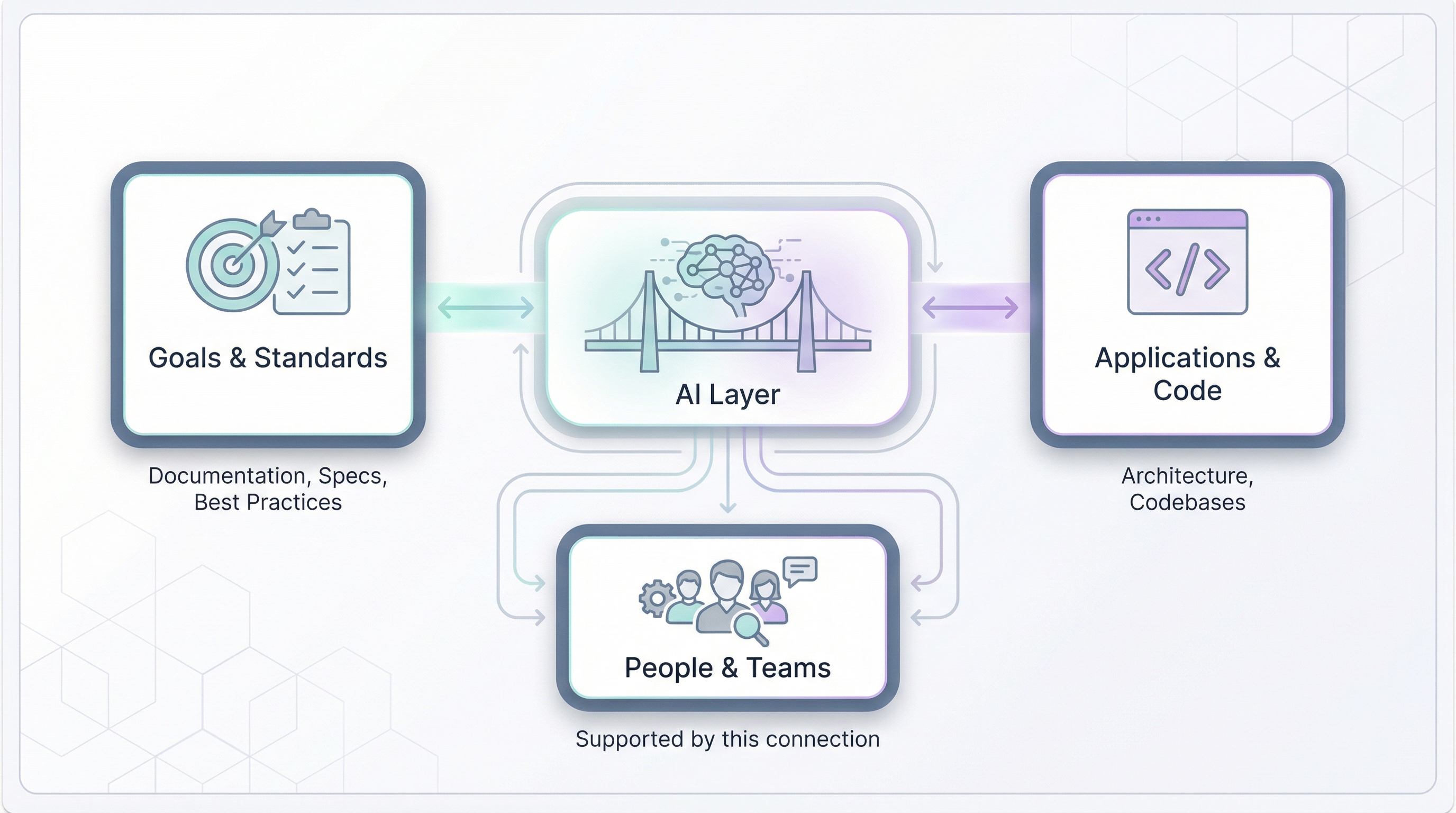
🧠 AI Orchestration
The AI Orchestration is the central piece of your AI-powered development workflow. It combines the AI Framework (your organizational knowledge) with AI Tooling (the interfaces developers use).
AI Framework
The AI Framework is a structured collection of knowledge, rules, and behaviors that define how your organization works. It’s not a product you buy — it’s something you build and maintain internally, tailored to your specific context.
Without an AI Framework, every AI interaction starts from zero. The AI doesn’t know your conventions, your architecture decisions, your preferred patterns. With an AI Framework, the AI becomes a team member who has read all the documentation and actually remembers it.
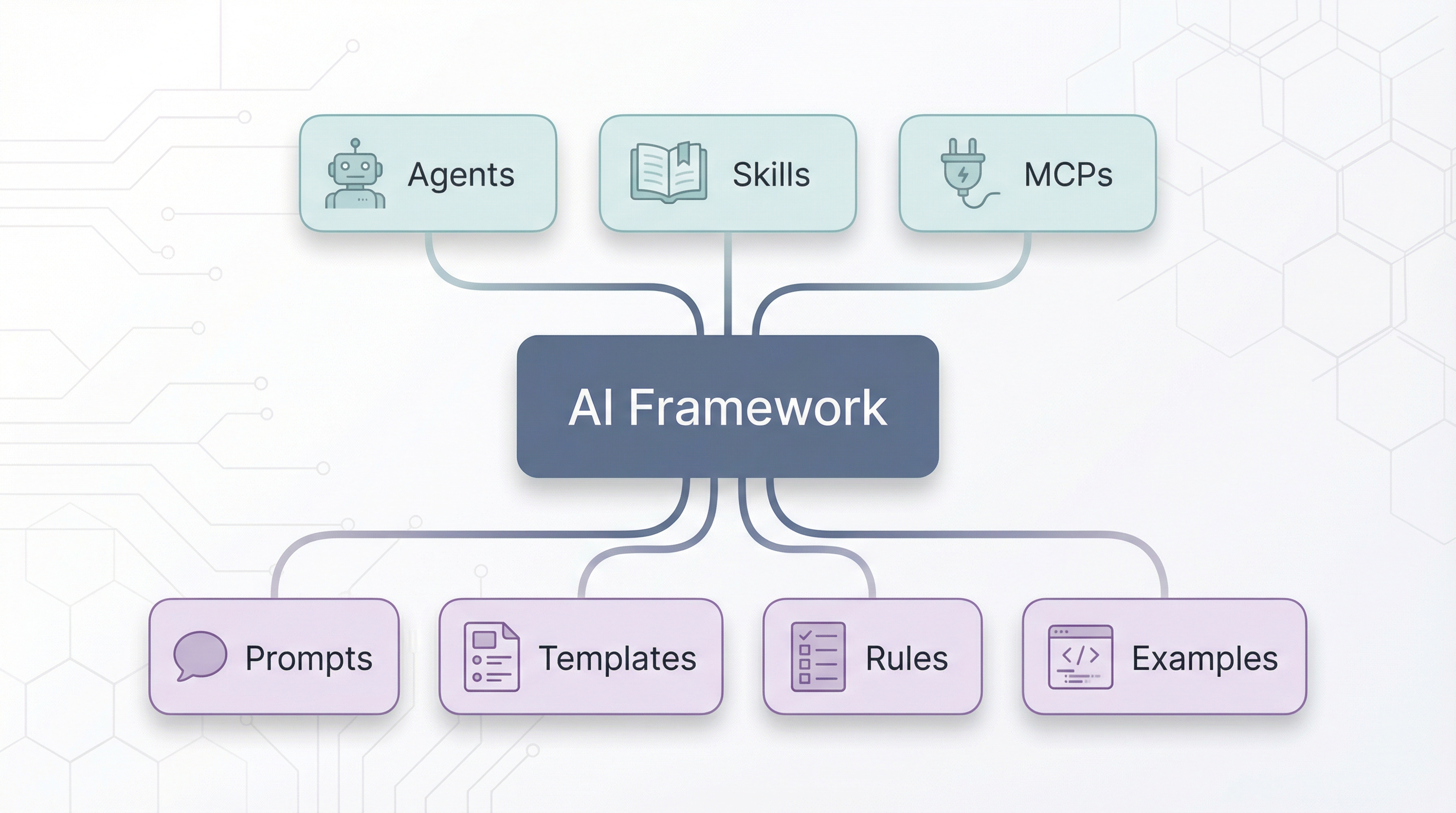
| Component | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Agents | Specialized personas with specific expertise | PM Agent, Frontend Agent, QA Agent |
| Skills | Auto-loaded context based on task type | Design system skill, API conventions skill |
| MCPs | Connections to external data and tools | Nx MCP, Jira MCP, Git MCP |
| Prompts | Reusable instructions for common tasks | ”When generating a component, always use our Button primitive” |
| Templates | Standard structures for common outputs | PR template, ADR template, user story format |
| Rules | Architectural constraints and conventions | ”Feature modules must not import from other features” |
| Examples | Reference implementations | ”Here’s how we structure a typical service” |
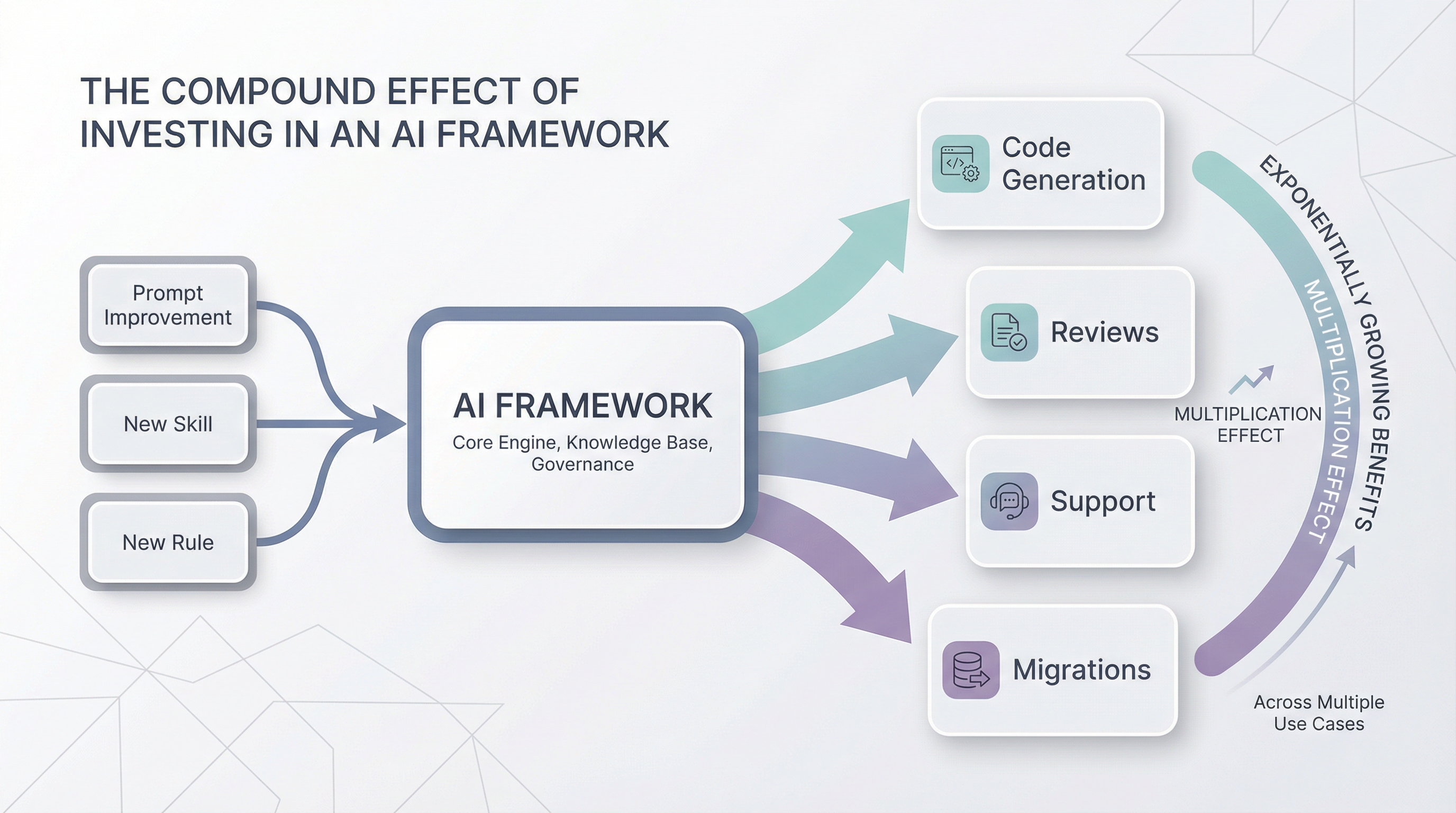
Your AI Framework is a living artifact. Every improvement you make benefits all use cases immediately:
- Discovered a better prompt for code reviews? Add it to the framework.
- New architectural pattern adopted? Update the skills.
- Common mistake happening? Add a rule to prevent it.
This creates a compound effect: the more you invest in your AI Framework, the more value you extract from every AI interaction.
AI Tooling
The AI Framework is consumed by multiple tools. Whatever tool developers use, they get the same AI behavior because they share the same framework.
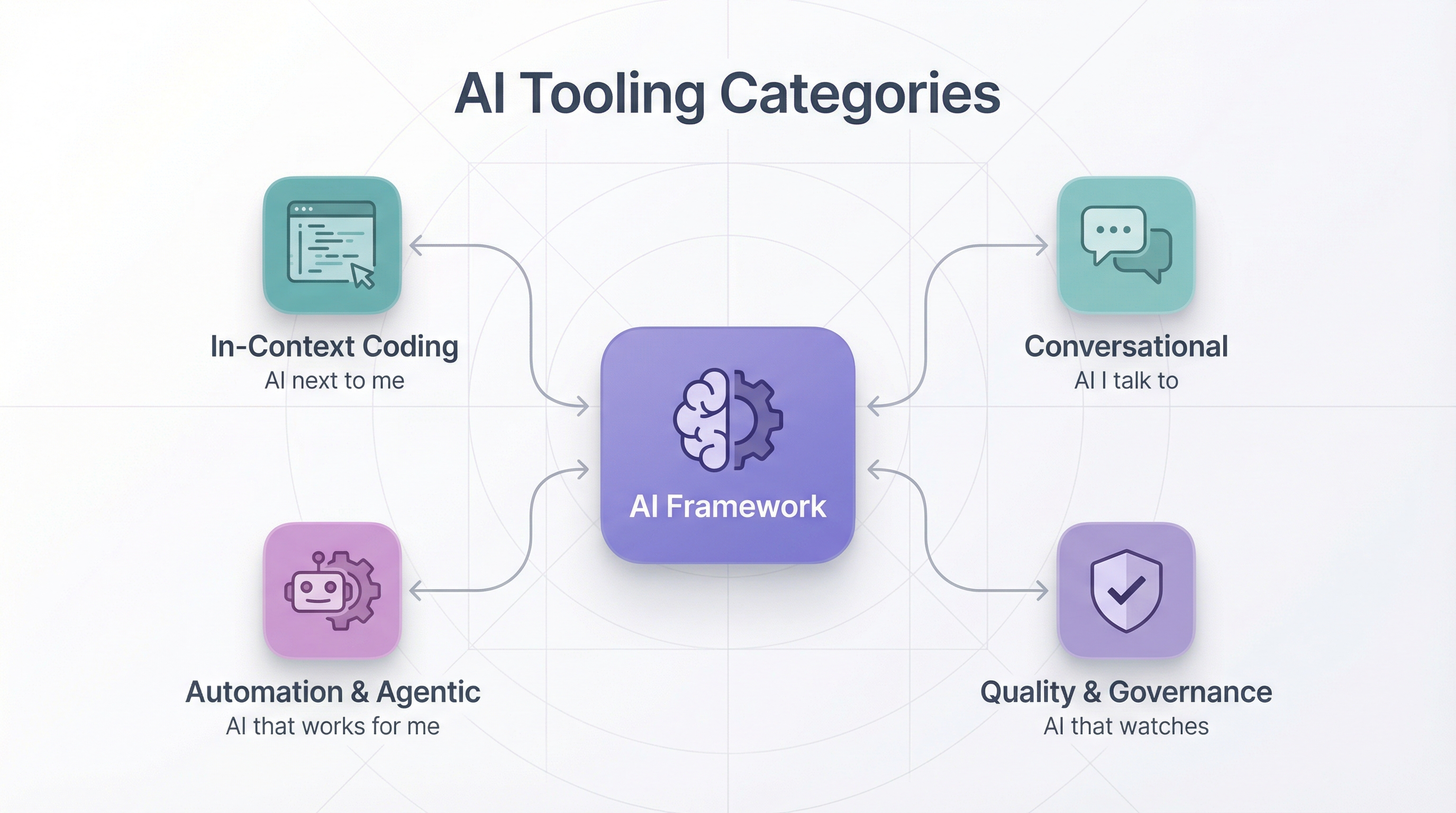
1. In-Context Coding Assistants — “AI sitting next to me while I type.”
IDE and editor integrations that help while you actively write code: code completion, inline refactoring, local reasoning over open files.
2. Conversational & Reasoning Tools — “AI I talk to when I need to think.”
Chat interfaces for understanding and decision-making: code explanation, debugging discussions, architecture reasoning, design exploration.
3. Automation & Agentic Tools — “AI that does work for me.”
CLIs and background agents that execute actions across the codebase: repo-wide refactors, scaffolding, feature implementation from prompts.
4. Quality, Governance & Delivery Assistants — “AI that watches the system.”
PR, CI/CD, and governance integrations focused on control and consistency: AI code review, test generation, CI failure diagnosis, architecture enforcement.
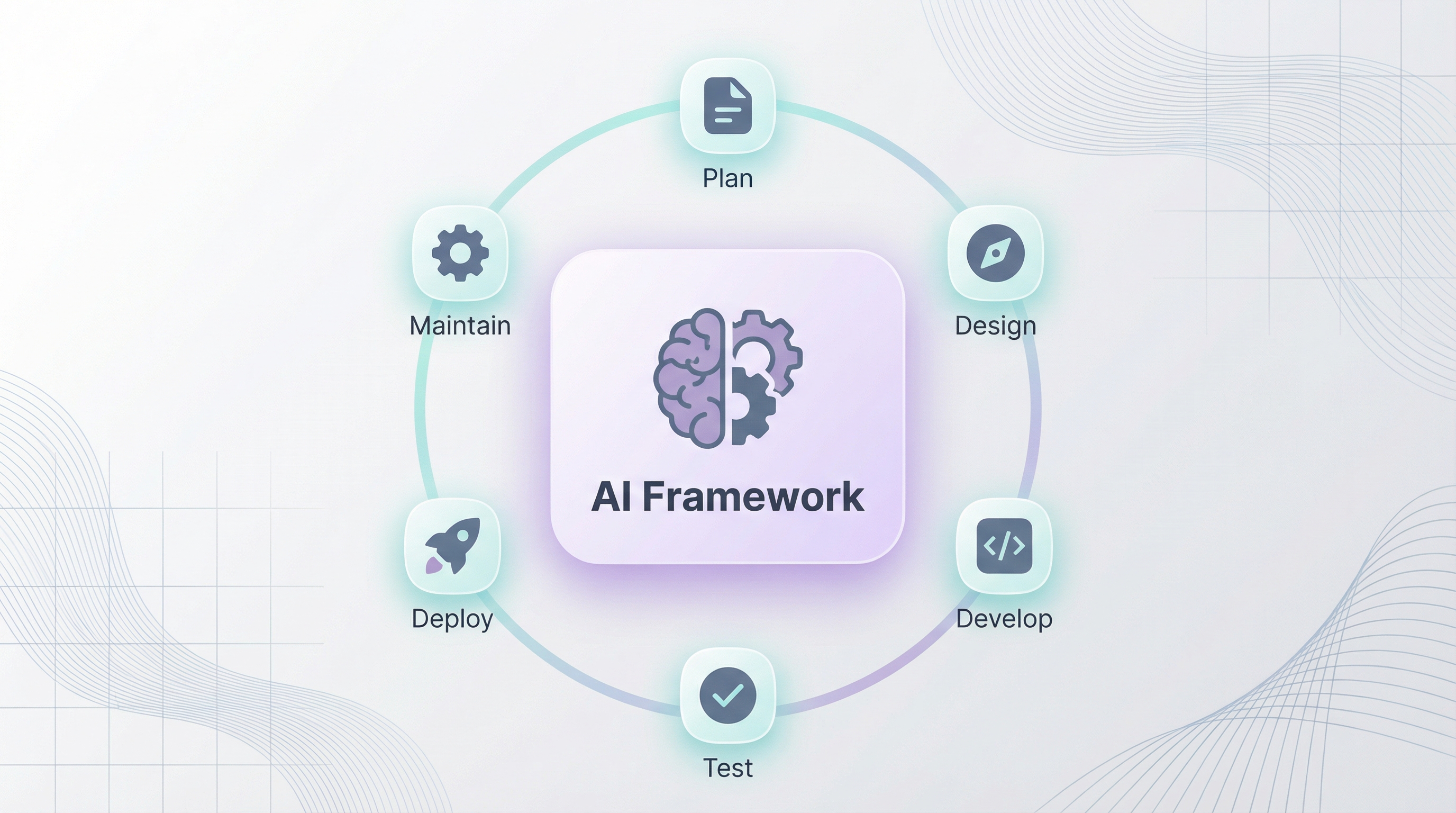
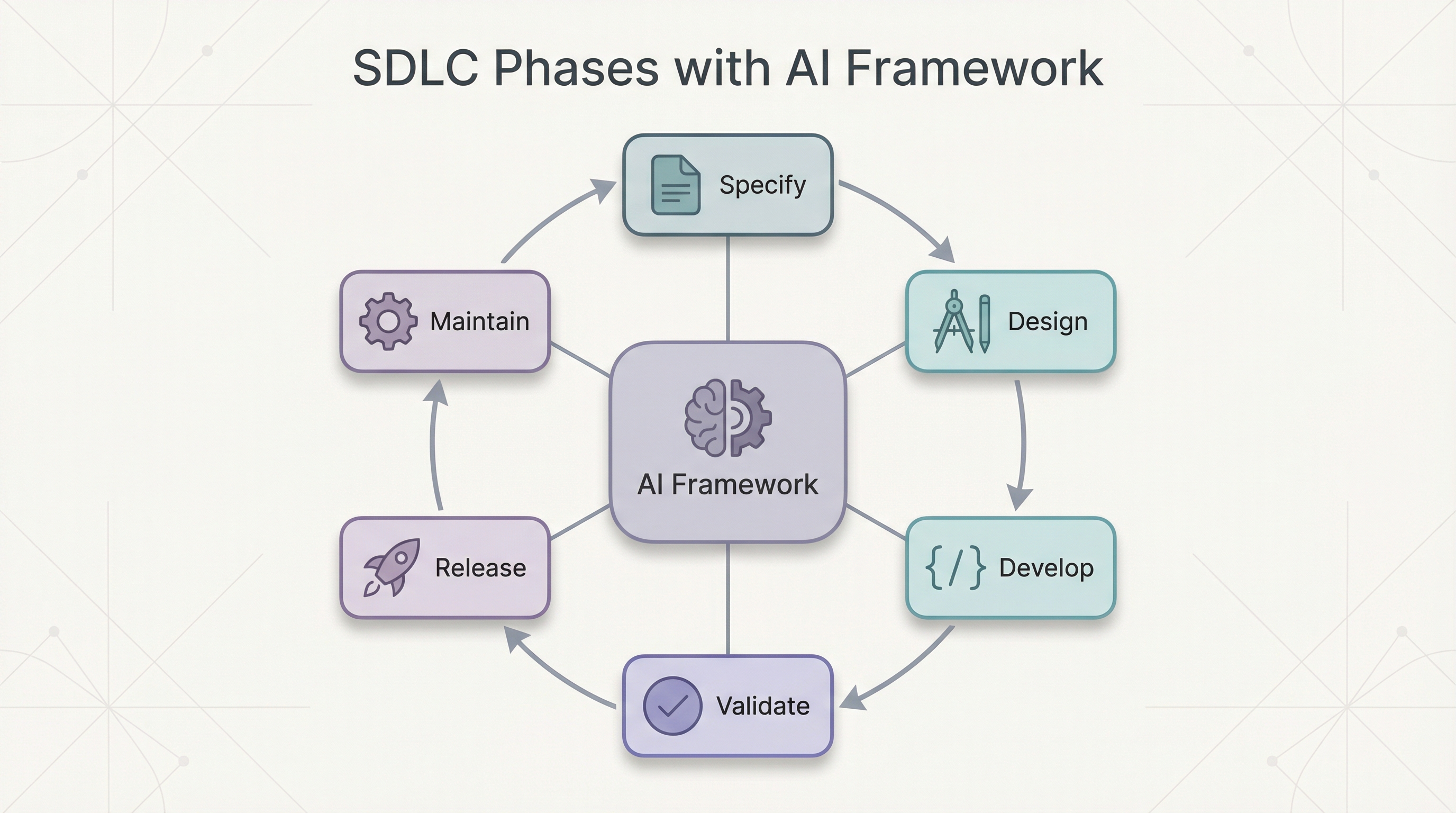
🎯 Developer Experience Across the SDLC
How does AI improve Developer Experience at each phase of the Software Development Lifecycle?
📋 Specify
AI supports Product Owners, Business Analysts, and developers in writing and refining requirements before any code is written.
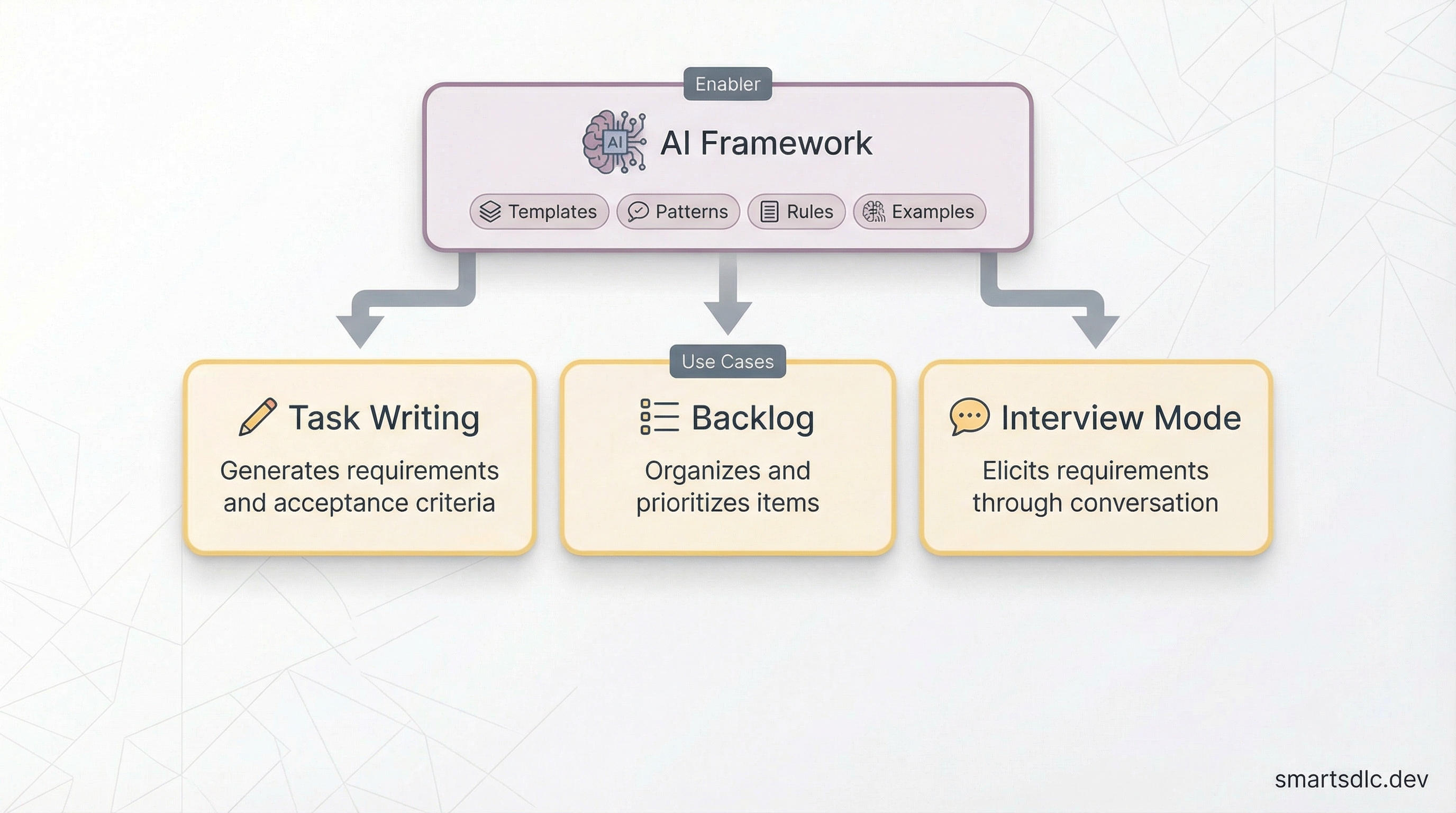
📝 Task Writing — Define your methodology (Agile, Scrum, SAFe) in your AI Framework with templates and acceptance criteria patterns. AI then writes tasks from rough descriptions, splits large stories, suggests acceptance criteria, and identifies gaps.
📊 Backlog Organization — AI analyzes your backlog to group related items, identify duplicates, suggest priorities based on dependencies, and flag stories that are too large or vague.
🎤 Interview Mode — Instead of writing specs from scratch, AI interviews you about technical details, UX decisions, and edge cases, then generates a complete specification.
Enablers
📝 Prompt Engineering Fundamentals
The model isn’t wrong — the prompt is. Whatever you want AI to achieve, you need prompts or specs it can understand and apply. Effective prompts include:
- Role: Who should the AI act as?
- Goal: What outcome do you want?
- Tasks: Step-by-step actions to achieve the goal
- Context: Background information about your environment
- Examples: Concrete samples that guide interpretation
📚 Recommended Reading: Google’s free ebook “Prompting guide 101: A quick-start handbook for effective prompts”
📄 Spec-Driven Development
Spec-Driven Development (SDD) flips the traditional approach: instead of writing code then documentation, you write the specification first and let AI implement it.
🎙️ AI-Assisted Spec Generation (Interview Mode)
One powerful technique is asking AI to interview you to generate a complete spec. Instead of writing everything yourself, you have a conversation:
read this @SPEC.md and interview me in detail using the AskUserQuestionTool about literally anything: technical implementation, UI & UX, concerns, tradeoffs, etc. but make sure the questions are not obvious
be very in-depth and continue interviewing me continually until it's complete, then write the spec to the file🏢 The BMAD Method
For enterprise-scale projects, the BMAD Method (Business Model Architecture Development) provides a structured approach with specialized AI agents at each phase:
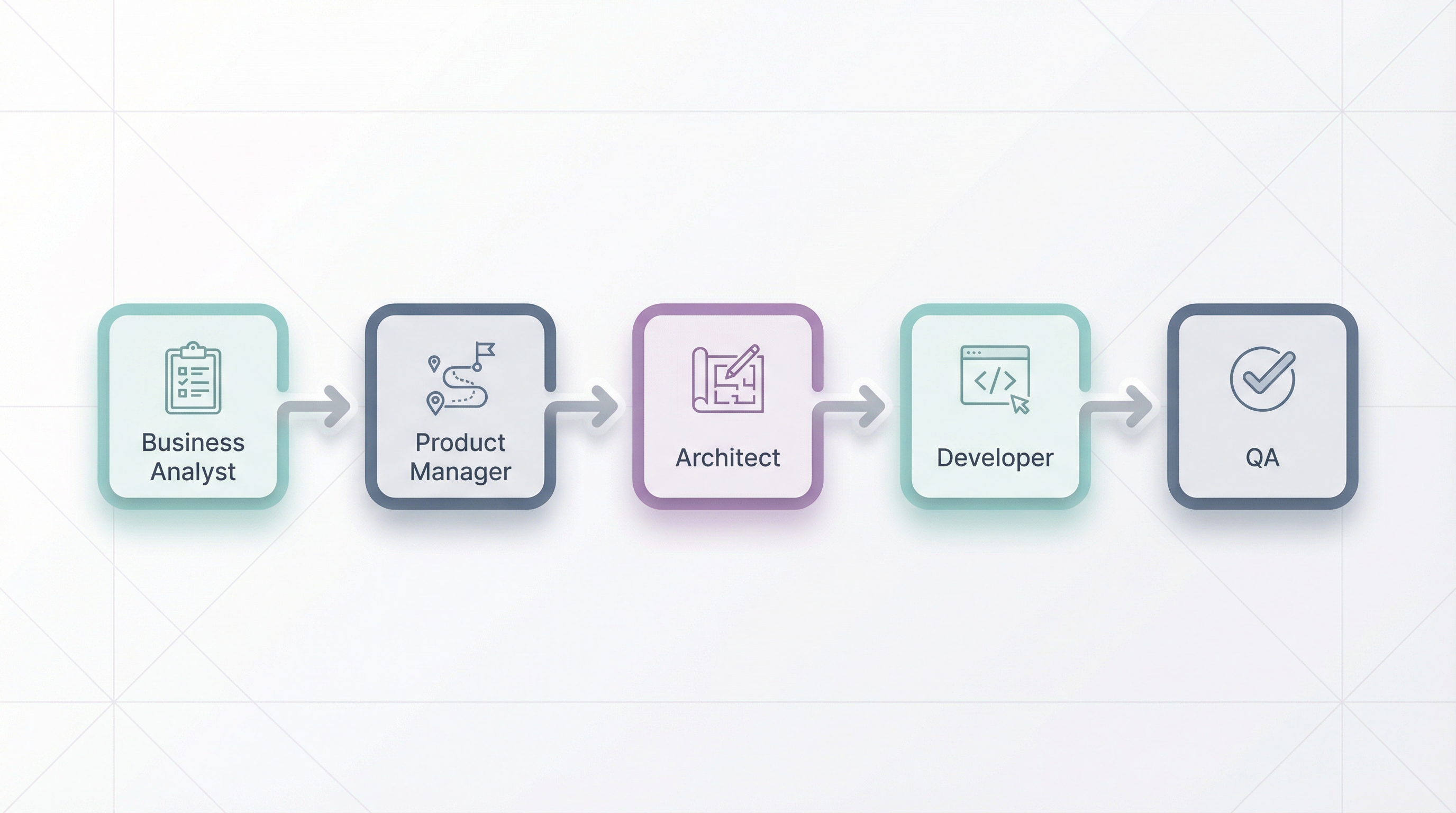
| Agent | Responsibility |
|---|---|
| Business Analyst | Requirements gathering, stakeholder needs |
| Product Manager | Prioritization, roadmap, user stories |
| Architect | System design, technical decisions |
| Developer | Implementation details, code structure |
| QA | Test scenarios, edge cases, validation |
Each agent has specific skills, context, and output formats tailored to their role. The output of one agent feeds into the next.
🎨 Design
AI helps design solutions that align with your existing architecture and patterns.
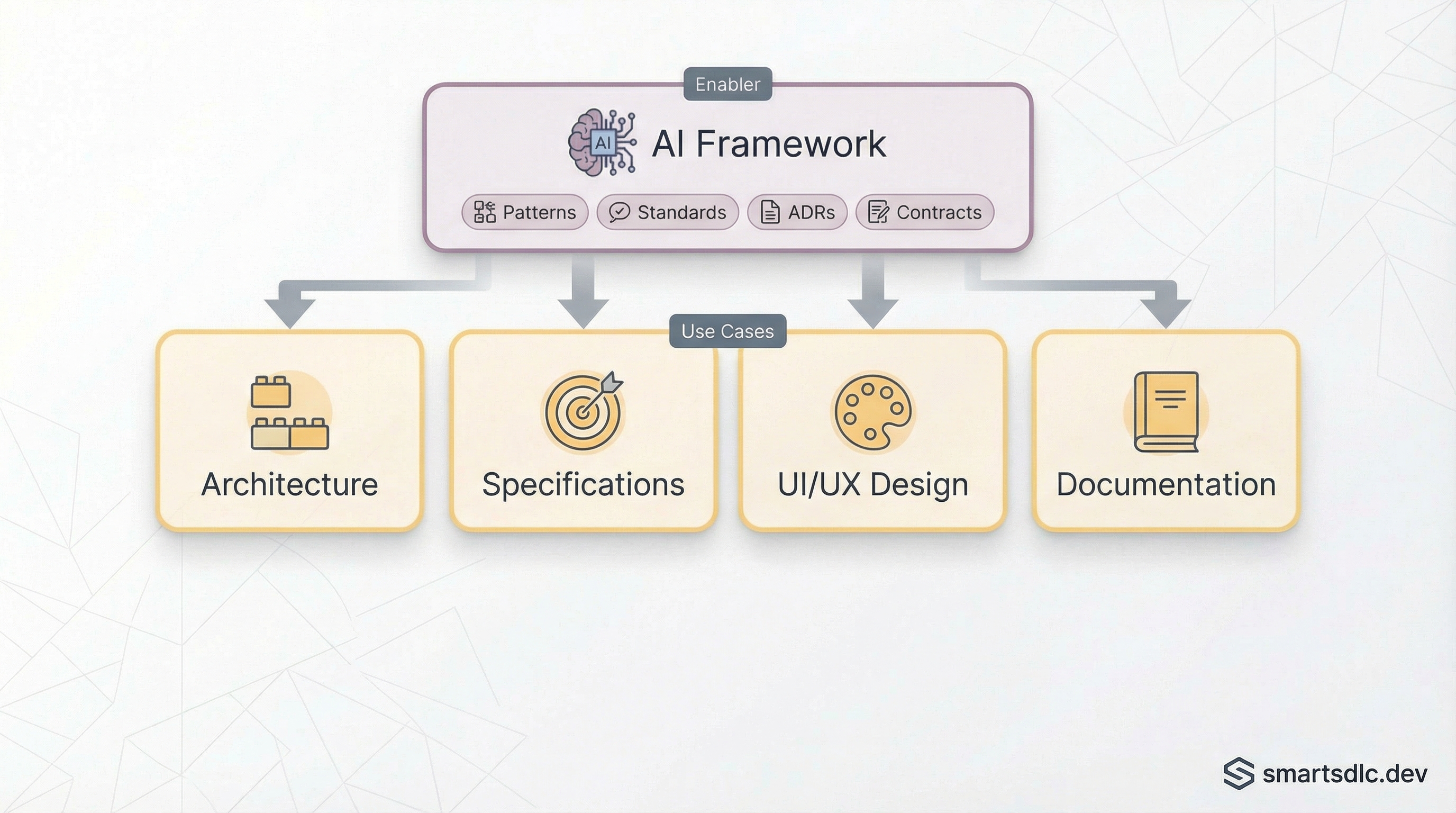
🏗️ Architecture Design — AI generates component diagrams, sequence diagrams, data models, API contracts (OpenAPI), and ADRs. When connected to your AI Framework, designs follow your established patterns — not generic solutions.
🎯 Specifications — From a high-level idea, AI produces detailed technical requirements, API contracts, data models, integration points, and non-functional requirements.
🎨 UI/UX Design — Generate mockups from descriptions, create variants for review, apply design tokens from your design system, and ensure accessibility from the start. Tools like v0.dev and Figma AI make this increasingly accessible.
📚 Documentation — AI produces documentation that stays synchronized: architecture overviews from code, API docs from OpenAPI specs, READMEs, and onboarding guides — all generated from source rather than manually maintained.
💡 Include your design system (components, tokens, guidelines) and ADRs in your AI Framework so AI respects past decisions.
Enablers
📋 Architecture Decision Records (ADRs)
Capture design decisions in a structured format AI can understand and reference:
# ADR-001: Use Event Sourcing for Order Management
## Status: Accepted
## Context
We need to track all changes to orders for audit and replay capabilities.
## Decision
We will use Event Sourcing pattern with Kafka as the event store.
## Consequences
- Full audit trail available
- Increased complexity in queries
- Need for event versioning strategyWhen ADRs are part of your AI Framework, new designs automatically respect past decisions.
🎨 Design System Integration
Your AI Framework should include your design system:
- Component library documentation
- Design tokens (colors, spacing, typography)
- Usage guidelines and patterns
- Accessibility requirements
💡 Storybook documentation can be exposed to AI, ensuring generated components match your established UI patterns.
💻 Develop
From autocomplete to full agentic coding, AI transforms how developers write code.
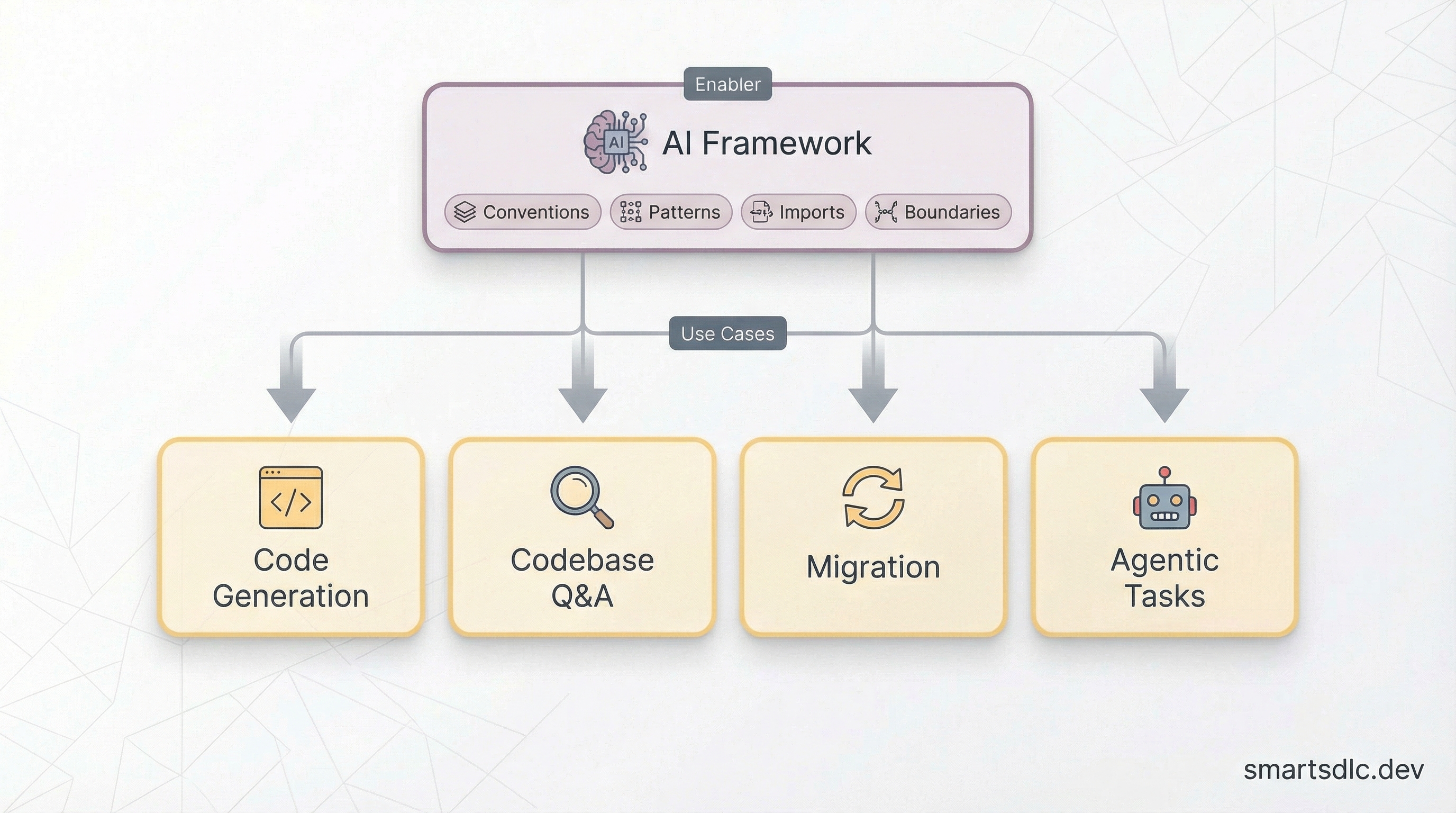
⚡ Contextualized Code Generation — Beyond generic autocomplete, AI with your AI Framework generates code following your naming conventions, established patterns, correct imports, and module boundaries. Generic AI creates new utilities; contextualized AI uses your existing @org/utils.
🔍 Codebase Understanding — AI helps navigate large codebases: “What does this service do?”, “What calls this function?”, “What will break if I change this?” Nx MCP provides project graph context for accurate impact analysis.
🔄 Legacy Modernization — AI accelerates codebase modernization: pattern detection, automated codemods, incremental file-by-file transformation, and continuous alignment with latest standards.
🤖 Agentic Tasks — Delegate multi-step tasks: “Create a new feature module with service, component, and tests” or “Refactor this class to use the new API pattern.” AI plans, executes, and validates.
Enablers
💻 AI-Powered Editors
Developers need editors with AI coding assistant capabilities. The AI Framework works across all of these — your skills and rules apply regardless of editor choice.
- AI-native editors provide deep integration: Cursor, Windsurf, Google Antigravity
- Extensions bring AI to existing workflows: GitHub Copilot, JetBrains AI
⌨️ Command Line Interfaces
CLIs are essential for automation, scripting, and CI integration. Three major players have emerged:
→ Claude Code — Pioneered concepts like MCP (Model Context Protocol) and Skills that are becoming industry standards. Its plugin system maps directly to the AI Framework concept, making it ideal for organizational standardization.
- MCP (Model Context Protocol) — Connect AI to external data sources: project graphs, issue trackers, git history, databases. Nx MCP exposes workspace structure, generators, and affected analysis.
- Skills — Auto-loaded context files based on task type. When working on a component, the design-system skill loads. When on an API, the api-conventions skill loads.
- Agents — Specialized personas with specific expertise that can be invoked for complex tasks (PM Agent, QA Agent, etc.)
- Prompts — Reusable instructions for common tasks that ensure consistency.
- Commands — Custom slash commands (
/commit,/review,/deploy) that trigger predefined workflows with consistent behavior. - Hooks — Event-driven automation triggered at specific points (PreToolUse, PostToolUse, Stop). Use them to validate actions, enforce rules, or run checks automatically.
- LSP (Language Server Protocol) — IDE integration that brings Claude Code capabilities directly into your editor with real-time suggestions and inline assistance.
→ Gemini CLI — Google’s entry adopts a similar approach with MCP support, bringing Gemini models to the command line with familiar conventions.
→ OpenCode — A really promising open-source alternative offering compatibility with multiple LLM providers (OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, local models). Great option if you want provider flexibility or need to run local models.
🔮 Future prediction: The line between editors and CLIs is blurring. We may move toward prompt-driven development where the interface matters less than the AI Framework powering it.
🔗 Agent Orchestration Patterns
For complex workflows, multiple specialized agents can collaborate:
→ Ralph Wiggum (Claude Code Plugin) — An orchestration layer that coordinates multiple Claude Code instances for complex, multi-part tasks.
→ Auto-Claude — Automated Claude Code workflows that can run sequences of tasks with checkpoints and validation.
→ Get Shit Done — A task-focused orchestration tool that breaks down complex objectives into actionable steps with AI assistance.
✅ Validate
AI can be both the creator and the validator — a powerful feedback loop where AI checks its own work and the work of humans.
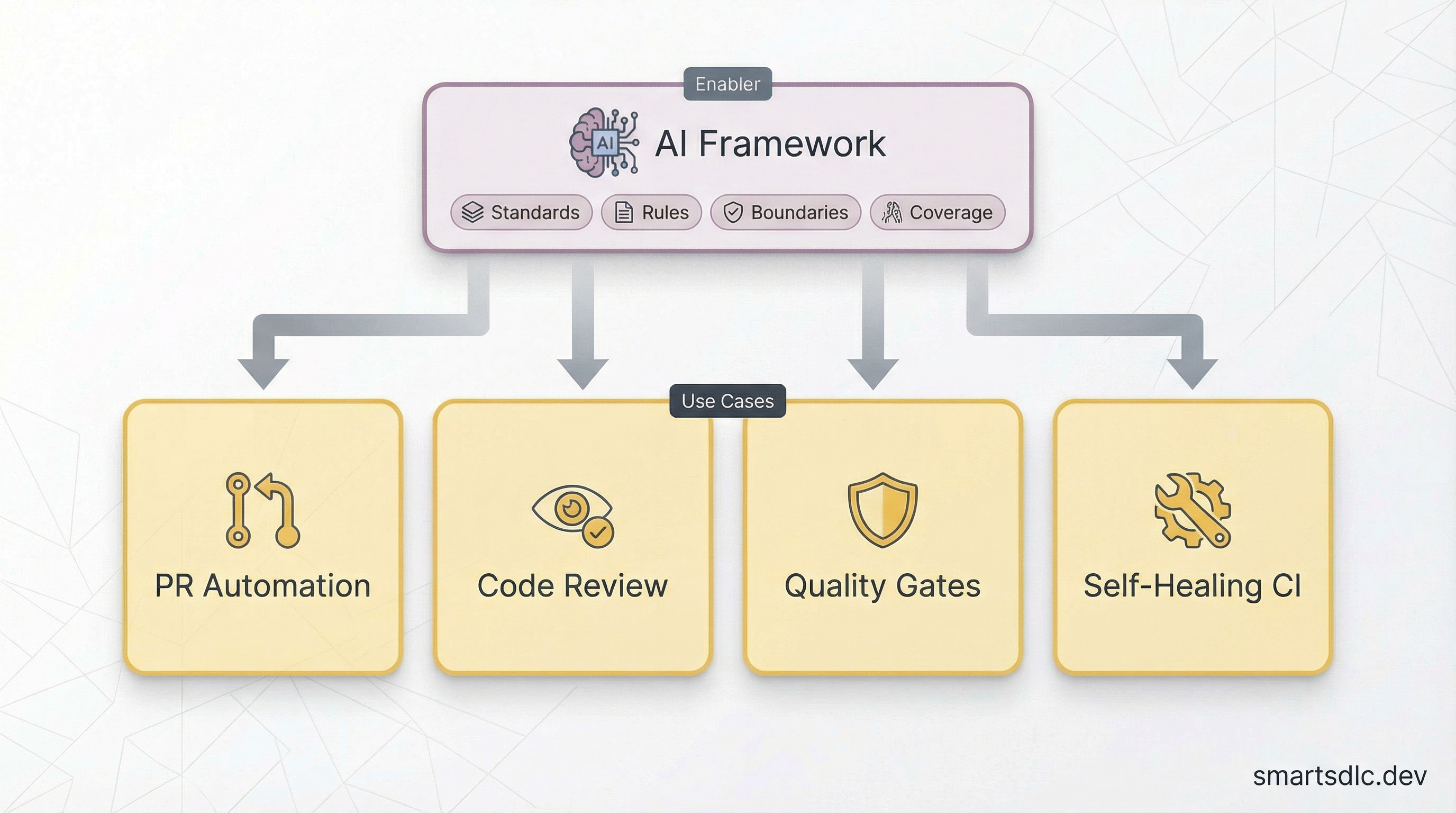
📝 PR Automation — AI analyzes diffs and commits to generate PR descriptions, list affected components, highlight risks, and fill templates. No more empty or “fixes stuff” descriptions.
🔍 Code Review — AI reviews PRs for pattern violations, security issues, performance concerns, and missing test coverage. Not a replacement for human review — a first pass that lets humans focus on design and logic.
🚧 Quality Gates — Automated checks block PRs violating module boundaries, unapproved dependencies, missing docs, or accessibility requirements.
🔧 Self-Healing CI — When CI fails, AI reads error logs, understands context, proposes fixes, and opens PRs. The flow is simple: CI runs and fails → AI agent analyzes error logs with codebase context → Fix is proposed as PR comment or auto-applied. Ask your CI questions in natural language: “Show me failed builds from last week.”
Enablers
🔧 Nx Cloud Self-Healing
Nx implements the self-healing pattern, connecting AI analysis with your project graph for accurate root cause detection.
🏛️ Architecture Conformance
→ Nx Conformance — Define and enforce architectural rules across your codebase: module boundaries, dependency constraints, naming conventions, and coding standards. AI can leverage these rules to ensure generated code respects your architecture.
🚀 Release
AI automates communication and coordination around releases.
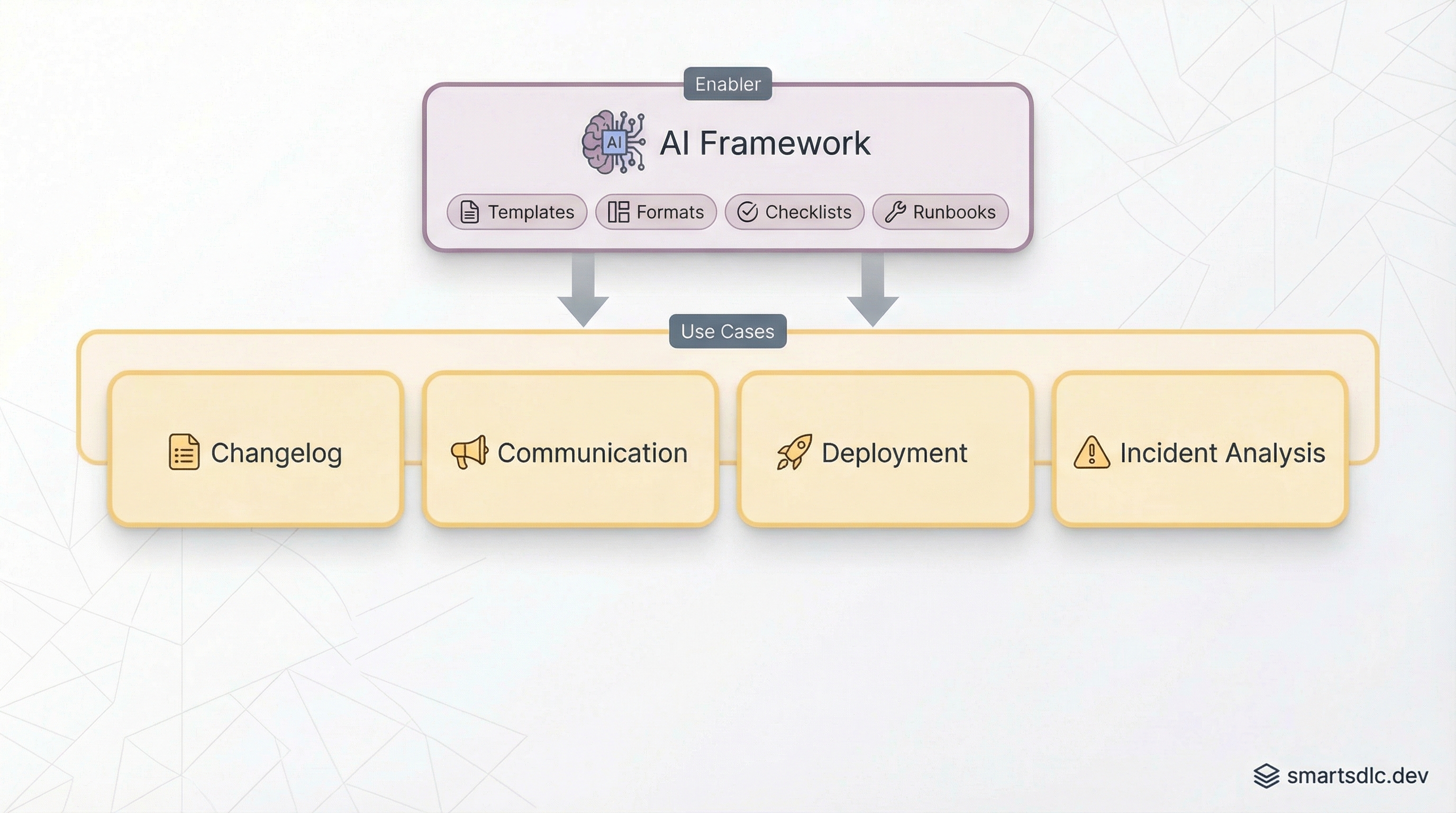
📋 Changelog Generation — AI analyzes commits and PRs to generate user-friendly changelogs, technical release notes, breaking change summaries, and migration guides. No more manually writing “what changed.”
📣 Release Communication — AI prepares stakeholder announcements, customer-facing updates, and team briefings — each tailored to its audience.
✅ Deployment Validation — Pre-deployment checklists, configuration validation, environment comparison, and rollback decision support.
🚨 Incident Analysis — When issues occur post-deployment, AI correlates with recent changes, analyzes logs, and suggests root causes or rollback.
💡 Use conventional commits (
feat:,fix:,breaking:) so AI can automatically categorize changes and determine version bumps.
Enablers
📝 Conventional Commits
Structured commit messages enable AI to understand changes:
feat(checkout): add express payment option
fix(auth): resolve token refresh race condition
breaking(api): remove deprecated v1 endpointsWith this structure, AI can automatically categorize and summarize changes.
📦 Automated Release Management
→ Nx Release — Integrated release management for Nx workspaces with version inference, changelog generation, and publishing. Combines conventional commits with project graph awareness for intelligent versioning across monorepos.
🔄 Maintain
Software is never “done.” AI helps maintain, improve, and evolve codebases continuously.
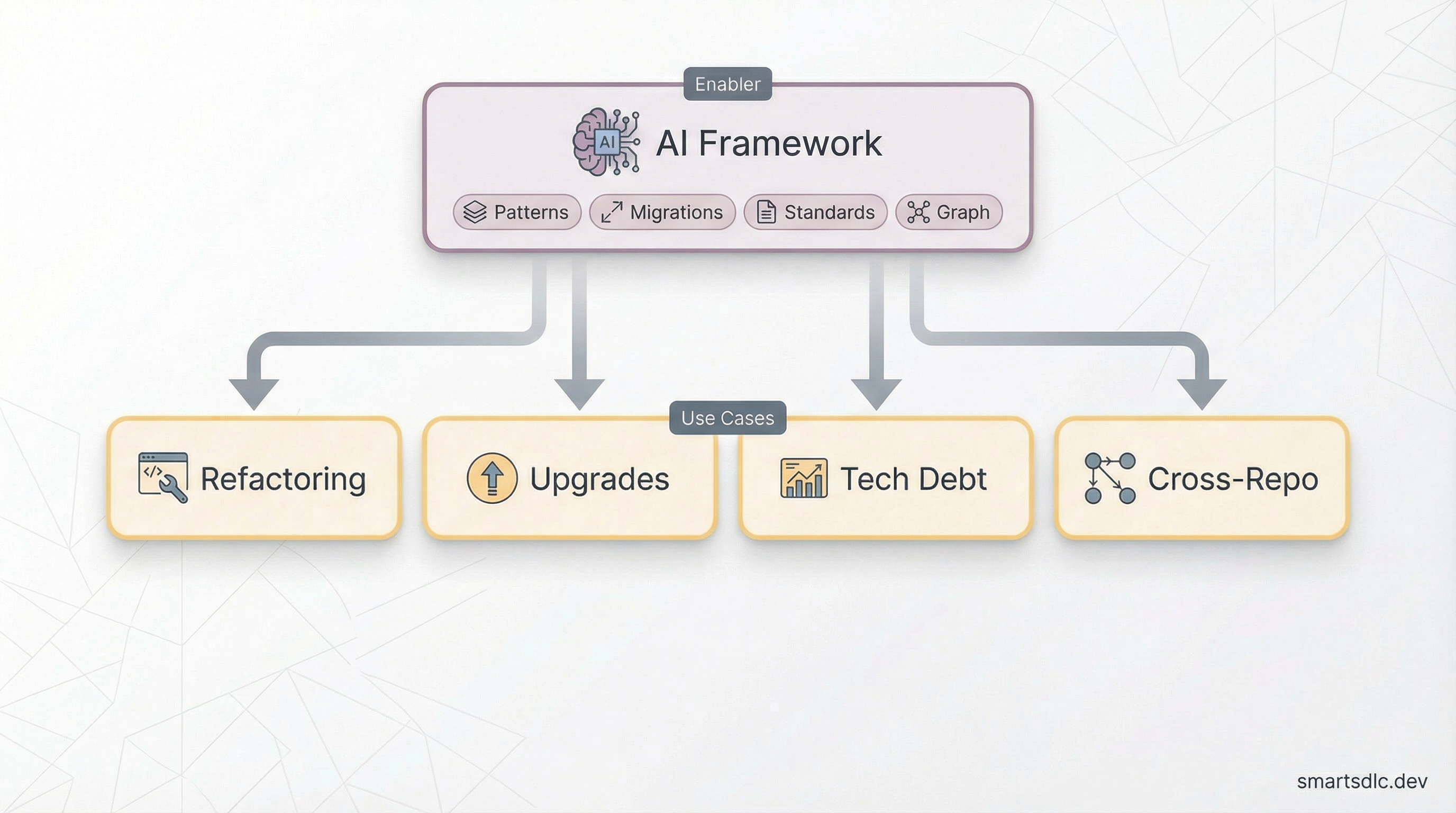
🔧 Automated Refactoring — AI performs large-scale refactoring: rename patterns, extract shared code, update APIs, remove deprecated code. With project graph context, AI understands impact and validates changes.
⬆️ Automatic Upgrades — When dependencies release new versions, AI reads changelogs, identifies breaking changes, proposes migrations, and validates with tests. Transform “dreaded upgrade sprint” into continuous updates.
📊 Tech Debt Analysis — AI identifies and quantifies tech debt: outdated patterns, missing coverage, complex code. Instead of “we have tech debt,” you get a prioritized list with effort estimates.
🌐 Cross-Repository Intelligence — For large organizations: understand dependencies between repos, coordinate spanning changes, ensure consistency. Nx Polygraph (coming soon) extends AI context across repositories.
Enablers
🔍 Code Health & Tech Debt Analysis
→ SonarQube / SonarCloud — Continuous code quality inspection that identifies security vulnerabilities, code smells, and tech debt. Provides quantified metrics and trends that AI can use to prioritize refactoring efforts.
🌐 Cross-Cutting Capabilities
Some AI capabilities span the entire SDLC.
📚 Living Documentation — Documentation that updates itself: API docs from code, architecture diagrams from project graph, guides reflecting current patterns. When code changes, documentation follows.
🎓 Accelerated Onboarding — New team members ask questions about the codebase, get architecture tours, and pair program with AI. The AI Framework ensures they learn your patterns, not generic ones.
💬 Automated Support — AI answers developer questions from documentation and resolved issues. Common questions get instant responses; only new issues reach the support team.
🔒 Security & Governance — Include security rules in your AI Framework: approved authentication patterns, required headers, prohibited practices. Track ROI with metrics on time saved and error rates.
💡 Start small, prove value, then expand. Training developers on prompting and building trust through gradual adoption is key to successful AI adoption.
Enablers
📖 Codebase Understanding & Documentation
→ CodeWiki (Google) — An AI-powered knowledge base that understands your entire codebase. Ask questions in natural language, get contextual answers with code references, and maintain living documentation that stays synchronized with your code.
🔧 CI/CD Intelligence & Optimization
→ Nx Cloud — Connects AI analysis with your project graph for intelligent CI/CD. Provides self-healing CI, pipeline analytics, task distribution insights, and cross-repository intelligence. Essential for understanding build patterns and optimizing delivery.
🏁 Getting Started
You don’t need to implement everything at once.
Pick one use case with clear ROI:
- CI painful? → Self-healing CI
- Onboarding slow? → Codebase Q&A
- Review bottleneck? → Automated review
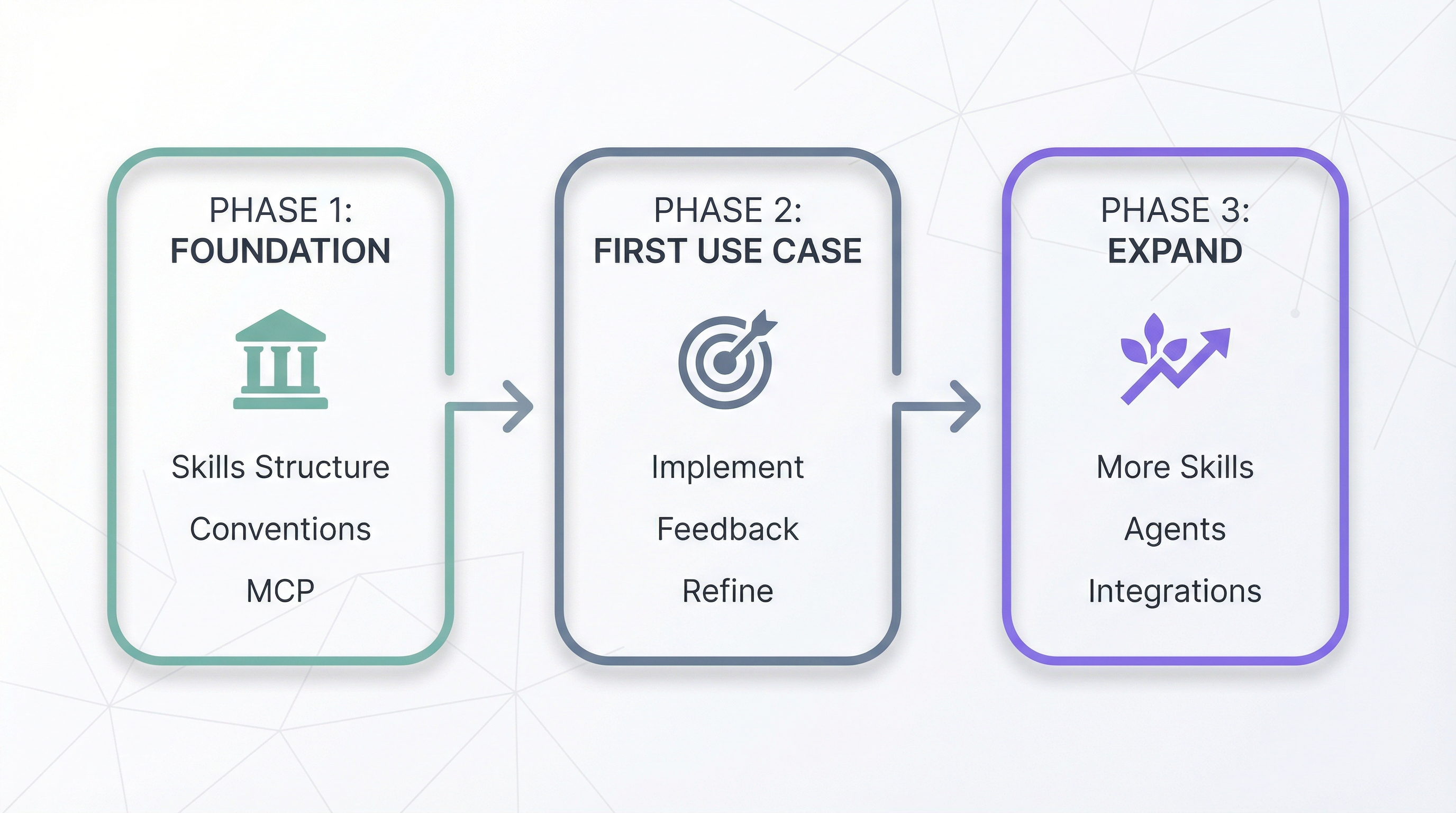
Build incrementally:
- Foundation — Create
/skillsstructure, document conventions, configure MCP - First Use Case — Implement, gather feedback, refine
- Expand — Add skills, agents, and MCPs progressively
Measure what matters: Time to first PR, CI resolution time, review turnaround, developer satisfaction.
🙂 Last Thoughts
AI is transforming every phase of the Software Development Lifecycle — from specification to maintenance. But the real power isn’t in individual tools; it’s in building an AI Framework that encodes your organization’s standards, patterns, and knowledge. When AI understands your context, every interaction becomes more valuable.
Key takeaways:
- AI Framework is central — Build it once, benefit everywhere. Your skills, rules, and MCPs work across all tools.
- Start with one use case — Prove value before expanding. Pick your biggest pain point and solve it well.
- Tools are interchangeable — Claude Code, Gemini CLI, Cursor, Copilot — your framework powers them all.
- Compound effect — Every improvement to your framework benefits all use cases immediately.
- AI augments, not replaces — Human judgment remains essential. AI handles the repetitive; you focus on the creative.
The organizations that invest in their AI Framework today will see compounding returns in Developer Experience, code quality, and delivery speed.
The question isn’t whether to adopt AI in your SDLC — it’s how fast you can build the framework to make it truly effective.
Want to go further?
If you're looking to improve your Developer Experience, build AI Frameworks, or optimize your CI/CD pipelines with Nx, feel free to reach out — I'm always happy to share real-world setups and practical tips.
Build on Foundations,
Scale with AI.
I design AI-powered workflows and engineering foundations that make teams faster, happier, and more consistent.








